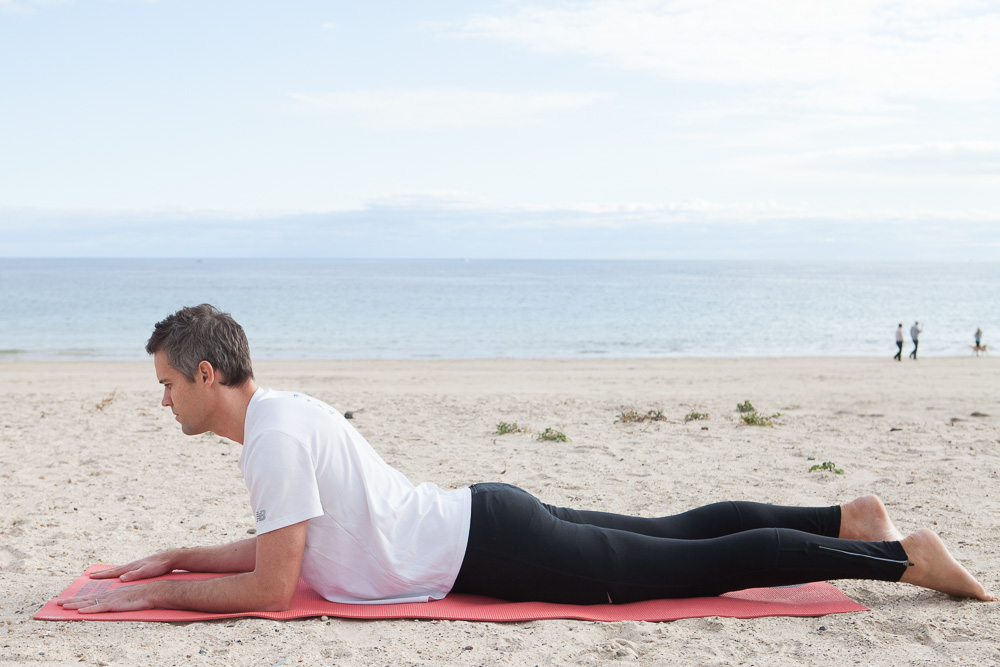
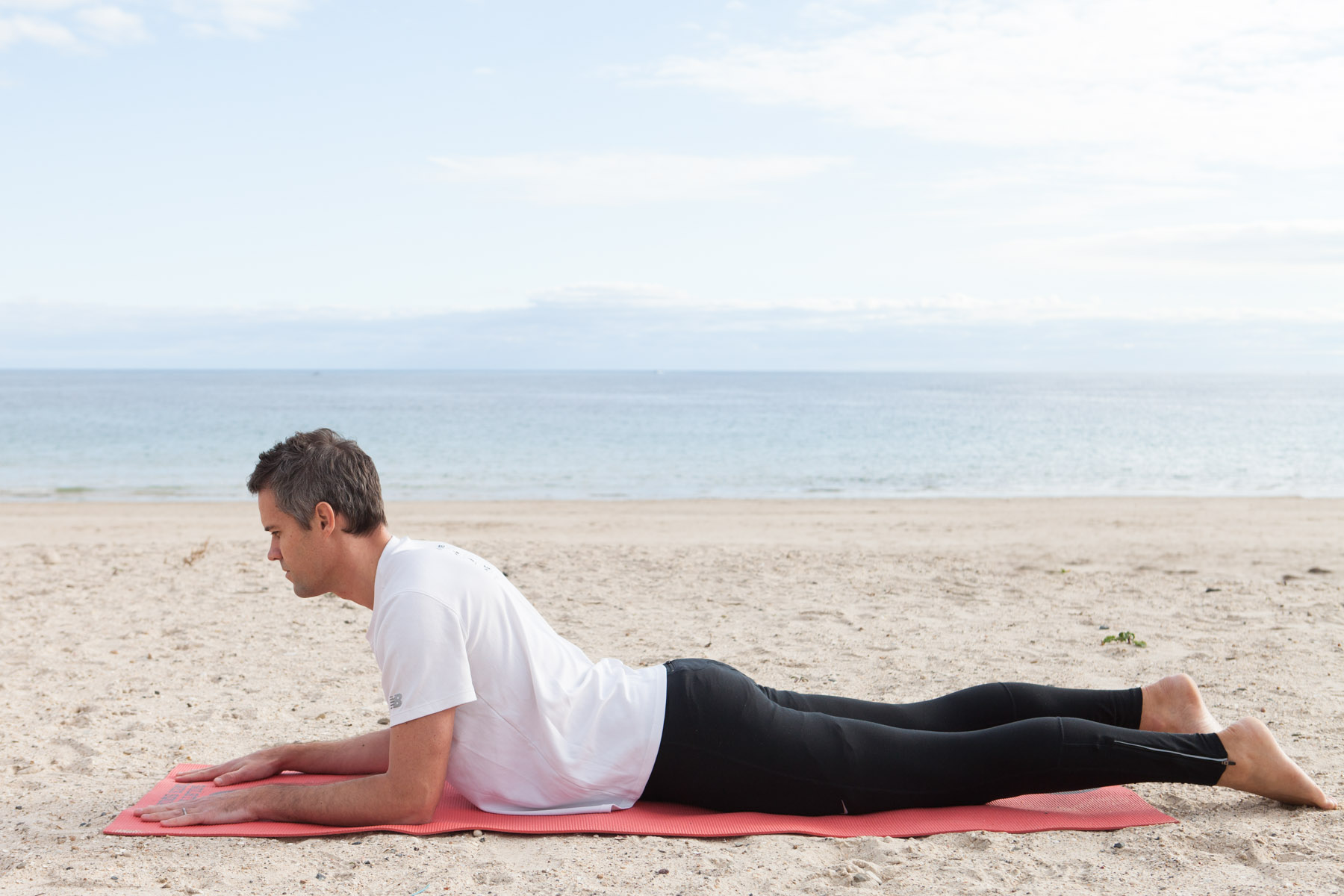
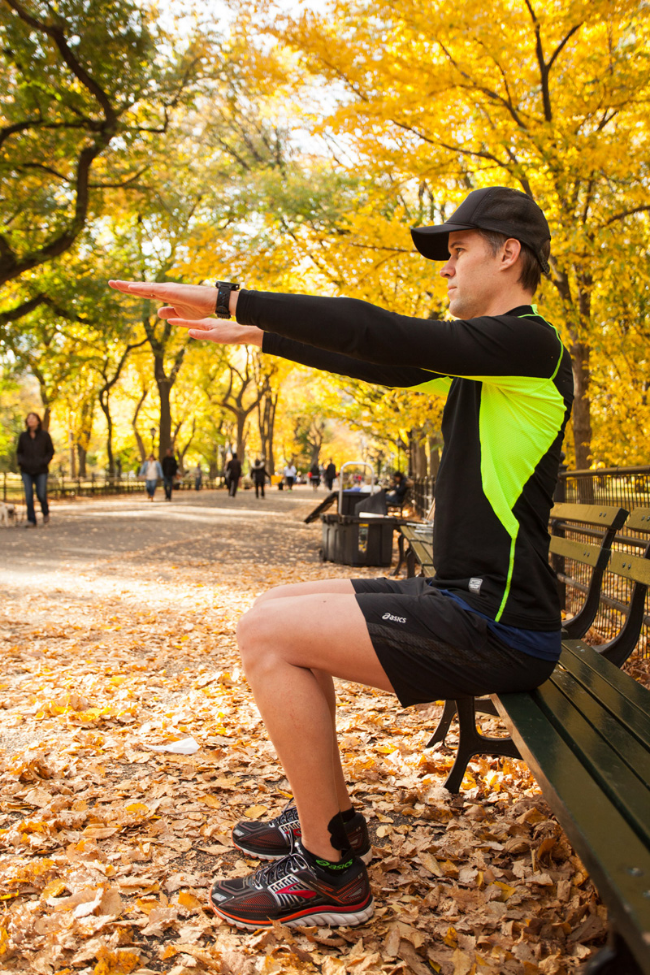
It's 'Global Running Day'... One of my fav exercises for runners, especially those with issues with their hips.
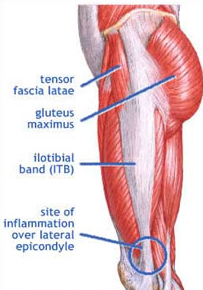
This drill will build capacity in the hip flexors (TFL, rectus femoris and iliopsoas), an important group of muscles for running.
Like the hamstrings, the hip flexors often end up in constant 'protective mode' due to weakness and lack of strength. Sitting all day tends to make them tight as hell.
This exercise will help get to the root cause of your tight hip flexors and also help to switch on your glutes.
Stand with theraloop around the middle part of your feet.
Drive one knee up so your thigh is parallel to the ground while also activating your core.
Important ➡️The weight bearing leg drives down⬇️ to the ground, strongly activating the gluteals. ✅This will help improve your running efficiency and gluteal activation on push off.
Happy Running!
#globalrunningday #runnersbody #runnersworld #runnersofinstagram #running #runningcommunity #resilientrunner #runforlife #runningtherapy #runninginspiration