The Power Of Plasticity - Helping You Move Better - Part 2
In Part 1 we talked about the power of neuro-plasticity and how it can work positively or negatively to affect your movement.
To summarize what we have learnt so far:
Dysfunctional Pain / Injury Cycle:
Ideal Pain / Rehab Cycle:
Pain changes the way we move
Research has clearly shown that people who are in pain change the way they move.
We see that people who are in pain (especially as it becomes more chronic):
move with less range of movement
move more slowly
have less variety of movement patterns available
show higher levels of muscle activity compared to people without pain
Muscle memory forms around these patterns and even though the injury often has healed (3 months average), you are left with changes in the way your body functions.
While these changes are obvious from a physical perspective, in order to get a full and accurate picture about what is going on, we need to take a broader view and see the bigger picture.
A shift in focus
The relationship between pain and the tissues becomes less clear the longer pain goes on (see picture below).
Credit: Explain Pain (Butler & Mosely)
As pain persists, we must consider the nervous system, and the plasticity that occurs around it.
When you have chronic musculo-skeletal pain, the two main issues from a nervous system perspective are:
altered body representation in the body maps in the brain (smudging)
reduced movement pattern availability (due to protection systems / fear of movement causing more damage).
Getting Personal
The best outcome will be when the clinician can spend a decent amount of time with someone in the beginning (at least one hour) to individually assess and determine an appropriate plan of attack to help the neuro-muscular system return to state of harmony.
One way to describe this approach is incorporating a top down (neurological based) and a bottom-up (local tissue) approach.
If you’ve been struggling with an ongoing pain issue, there is good news. A large body of research shows the more you can understand about the nervous system and why you’re in pain, the more likely you’re going to make a full recovery. I’d highly encourage you to talk to your local Physio or GP about some specific resources that can help you in your journey.
In Part 2 of the blog, we go into depth about how to optimise your lifestyle to enhance the effects of neuro-plasticity and reach your movement potential.
I hope you find it useful, (and I welcome your questions in the comments below).
1. Aerobic Exercise
I like to think of changing our neuro-muscular habits as similar to the process of creating glass.
Sand is heated up to very high temperature, and then molded and then left to set in a certain desired shape.
The most important part of this process is the heating, where the sand becomes malleable, pliable and able to be worked into a particular shape.
Without the heat, there is a stiff, solid structure with no ability to change.
Our brains and bodies work in a similar way.
In terms of changing our neuro-muscular patterns, aerobic exercise is what creates a similar heat-like environment for creating brain/movement plasticity.
Aerobic exercise (especially running) has shown to strongly increase blood flow to the brain, decreasing inflammation and even stimulating new brain cell growth through the expression of neurotrophic factors (such as BDNF and IGF-1).
Physical exercise facilitates neuroplasticity
An article by Hottling and Roder in Neuroscience and Behavioural Reviews explains the benefits of physical exercise on neuroplasticity.
The authors conclude that increase in cardiovascular fitness has significant neurocognitive benefits.
The hardest part is to begin
If you haven’t moved much for months or years due to pain or general inactivity, your ability to re-wire your movement becomes much more limited.
If you’re already in pain and find movement difficult, a downward spiral can quickly unravel (see picture above).
Getting moving can be tough, but just remember, 90% of the fuel is to get the rocket off the ground is used in the first 2 minutes.
Breaking through movement inertia is hard work, but once you get going, things get much easier and you have made the most important first step in feeling better again.
Guidelines for aerobic exercise if you’re in pain:.
Find something you enjoy and that you could maybe do with a friend to keep you accountable
Start with an easy level (less than 5/10 intensity) You should be able to talk to a friend at your easy pace
Pace yourself. Take short breaks as you need to before you get fatigued
Monitor your 24 hour response and progress gradually as you can
Set up a positive reward immediately following - a nice healthy meal or watch your TV show
Make it fun and playful
Listen to your favourite music or podcast
I would recommend, if you are trying to improve your neuro-muscular patterns, that you spend at least 30-60 minutes per day engaged in low-moderate intensity exercise.
Running stimulates neuro-plasticity
Running deserves a special mention here because I think the process of learning to run can be one of the best things you can invest your time in, in terms of building your foundation through neuro-plasticity.
One of the great things about running, (providing you can learn to listen to your body), is that it gives you ongoing feedback to where your weak links are.
For example, you might be out running and you feel your hip getting tight. After your run, you focus on some specific hip stretching and release exercises. The next you run, your hip feels great.
And then you get a bit quicker and can longer, but then your hamstring starts playing up. Once again you go back and do some hamstring strengthening and once again return to running more resilient and stronger than before.
This process can take weeks, months or years, so patience is required. But always keep in mind where you started from and seeing the progress you are making should be enough motivation to fuel your onward progress.
One of the other great thing about running is the concrete goals you can set and build towards such as 5k Park runs, 10km community events or marathons in exotic locations around the world.
There is an amazing running community that can help support you also.
2. Food
The four most outstanding foods for increasing neuro-plasticity are blueberries (high in flavinoids and anti-oxidants), omega-3 fatty acids, green tea and curcumin (found in turmeric). It’s worth considering making these a part of your regular diet.
An abundance of fresh vegetables and fruits
The best vegetables are those that are non-starchy (low carbohydrate content) with high amounts of fiber. Fiber gives us a “full” feeling and keeps the intestinal tract moving. Low glycemic fresh fruits, fresh vegetables in salads and cooked vegetables should provide the bulk of the food in an optimal neuro-plasticity diet.
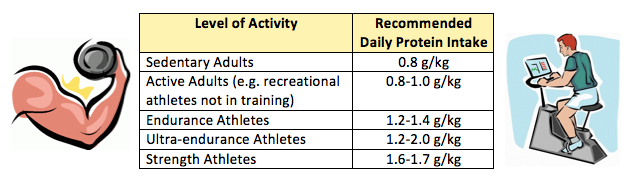
Protein
Re-building neuro-muscular patterns requires additional protein, compared with a sedentary person.
The timing of the protein is also critical, with research showing that evenly spreading your protein over 3 or 4 meals during the day creates the best environment for recovery and re-building.
High quality fats
Healthy fats make up a critical part of a good neuro-plasticity diet (the brain consists of nearly 60% fat).
These include:
omega-3s (from high quality fish high in omega-3s, flaxseed, grass-fed beef, eggs)
monosaturated fats (from extra virgin olive oil, avocadoes, nuts, and seeds)
medium chain triglycerides (from extra virgin coconut oil)
saturated fat from (grass-fed meat, eggs and milk, yogurt, cheese)
Coconut oil excels as cooking oil, for it doesn’t oxidize at high temperatures. Cooking with butter, or even better with clarified butter (called ghee in India) is another safe alternative to vegetable oils that go off at even low heat.
Reducing unhealthy fats especially trans fats and most vegetable oils except extra virgin olive oil is important.
Low sugar and carbohydrate intake
Fruits with a high fructose content are best eaten sparingly in a healthy neuro-plasticity diet.
These include:
mangoes, peaches, pineapple, plums and grapes.
fruit juice is equal to soft drink in sugar content so should be avoided if possible
3. Sleep
Getting enough sleep is a critical part of creating optimal neuro-plasticity.
Research shows adequate, quality sleep and synaptic plasticity are strongly related.
Your brain needs sleep to reset brain connections that are important for memory and learning.
If sleep is an issue for you, SA Health have a useful guidebook you can download here
4. Positivity and Self-Belief
“Beliefs create biology” - Norman Cousins
When you’re find yourself in pain, one thing you have to commit to is not allowing yourself to entertain negativity in your life.
Repeating a few key positive words or mantras to yourself can help you work through a rough patch.
Some of my favourites include:
“My spine is strong and resilient'“
“This is like a storm, it will pass, I’ve just got to get take some extra care of myself until it passes”
“Wounded but not conquered”
“Motion is lotion”
Part of being positive is to have realistic expectations and to expect set backs and a non-linear recovery.
5. Variety of Movement Wins
People who are in pain, often describe they feel like they are moving like a robot.
They get ‘stuck’ in a certain pattern and can have a tough time breaking free, as well as adapting to their environment.
Creating new movement patterns is like learning new chords on a guitar.
The more chords you know, the better your music will sound.
How do we develop Movement Programs?
If you ever saw the movie, The Matrix, you may remember when Neo ‘learns’ how to do kung-fu in a matter of seconds via an upload to his brain.
While science fiction now, the principles are the same. We need to upload the appropriate movement patterns and skills that are going to give us the best chance of achieving success.
The difference is that motor learning and skill formation takes a little longer in real life compared with a few seconds in the movies!
The initial process of learning and practicing a skill can be very mentally taxing.
Author Malcolm Gladwell stated around 10,000 hours was needed to develop high level of skill and used the example of the Beatles, in the early 1960’s, played in Hamburg where they played 5 hours per night for 270 nights over a couple of years. That intense level of practice turned them into the success they were.
If 10,000 hours seems a bit far-fetched, there is good news.
Researches believe, to install a new pattern or habit, you simply must practice it sixty times every day for 21 days in a row.
In terms of movement, this sounds very achievable.
For example if you’ve got a sore your back, you may have lost the movement patterns of:
pelvic tilting
hip hinge
squatting
If I get you to practice these movements everyday, you will start to re-groove these patterns back into your body/mind, and soon they will be stored sub-consciously, ready to use during the day when needed.
The more variety of movement patterns you have available and online ready to use, the more the load is spread evenly through the body, not always relying on the same pathway to get the job done.
6. Dry Needling / Massage
We know dry needling works by increasing blood flow and directly improving the flexibility of the muscles.
However, some new research is coming out showing dry needling improves kinesthetic sense and effects helps to sharpen the sensory homunculus, leading to improved awareness, flexibility and joint range of motion.
This study showed how needling can re-wire the somato-sensory cortex (body maps) in the brain with people with carpal tunnel syndrome. The research suggest that improvements in primary somatosensory cortex sharpness can predict long-term clinical outcomes for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Studies have shown that dry needling also increases the release of nerve growth factor, which aids in rewiring the brain for improved motor patterning and decreasing the loss of brain smudging to areas of chronic pain.
There is a lot of research still to be done and it must be stressed this is still in the speculative stage. However, to me this line of thinking is very plausible and opens up an exciting frontier for the all rehabilitation professionals.
The ability for the needle to get in the deep parts of the muscle provides a significant sensory stimulation that can help create improved movement efficiency and awareness.
Massage and foam rolling can also have a similar effect, although more superficially.
7. Relaxation / Recovery
Stress is one of the main factors that decreases neuro-plasticity in the adult brain.
Cortisol is one of the chemicals that chronic stress can produce and makes forming new synaptic connections very difficult.
When you’ve had a pain or injury, our default mode is often fear and anxiety and this can lead to being constantly on the look out for potential threats (real or perceived) that could disturb our safety.
Going through a traumatic event, (or repeated mental, physical or emotional trauma over many years) can create a deep neural pattern of self-protection.
This can look like constant muscle tension / guarding and severe physical de-conditioning over many years.
Everyone is different, but learning to get your body back into a relaxed state (para-sympathetic) is a really important part of your healing.
It could involve things like:
relaxing warm bath
hike in nature
going for a swim or surf
restorative yoga class
getting a massage
deep breathing exercises
talking with a friend
going to the movies
knowledge can be empowering and educating yourself about your body and the pain process can be a liberating experience
Try and make a list of things that relax you and schedule them into your week ahead of time.
8. Tips to Improve Body Maps
Movements that are most likely to lead to changes in the quality of the maps are movements that are different, interesting, rich in sensory input, slow, gentle, mindful and non-painful.
Walk barefoot on the grass and feel your foot moving on the ground
Roll a spikey ball under your foot
Watch your favourite athlete move
Tai chi, Pilates, Feldenkrais, Somatic therapy, Alexander therapy and yoga are all recommended
Mirror Neurons
Have you ever wondered why your tennis game suddenly improves after you’ve watched two weeks straight of the Australian Open?
Welcome to the world of mirror neurons.
When we watch someone else doing something – swimming, picking up a newspaper, eating – we also simulate with the body maps in our brains what it might feel like for us to be doing those same things.
Personally, I find the night before a run, watching some youtube clips of elite runners helps get in the zone.
For runners, I’d highly recommend:
For tennis players:
For footy lovers:
Take Home Messages:
The body grows best when it is challenged and stressed at the right rate with the right conditions (exercise, diet, sleep, recovery).
Change takes time and to build and re-wire new movement patterns takes, at minimum 3 months, on average 12 months.
Considering a top-down (neurologically brain-based) and a bottom-up approach (local muscular level) can bring about some dramatic shifts in how we go out understanding how to move better.
Patients must be treated on an individual basis, and clinicians should target both mechanical and neurological deficits as they are indicated for a particular person.
If you can harness the power of your mind, you can achieve things you may never though possible and surpass limitations that have been holding you back.
Hopefully this blog post will help you think beyond the muscles, joints, and ligaments to what is happening in the nervous system to improve your movement.
If you’ve made it this far into the blog post, a big congratulations!
I know it’s been a long haul and I apologise for not being more articulate in my message.
The fact is I think about these things a lot, and trying to communicate this information in a brief 1:1 Physio consultation just isn’t possible.
Please let me know if you’ve found any of this useful in the comments below.
Recommended Reading:
All About Running: Synaptic Plasticity, Growth Factors and Adult Hippo campal Neurogenesis
It is not just the brain that changes itself – time to embrace bioplasticity?
Smudging of the Motor Cortex Is Related to the Severity of Low Back Pain
Smudging the motor brain in young adults with recurrent low back pain.
Disrupted Tactile Acuity in People With Achilles Tendinopathy
Primary Motor Cortex Organization Is Altered in Persistent Patellofemoral Pain
Alteration in global motor strategy following lateral ankle sprain
Introducing, KIN Foundation (Physio Group Class):
KIN Foundation Pilates is designed to truly encompass a top down (neuroplastic) and a bottom up (physical movement) based approach to therapy.
KIN is an acronym for:
Kinesthetic (optimising sensory input to sharpen body maps in the brain)
Integrative (having uniting and positive effect on all systems of the body)
Neuro-muscular (fine tuning the muscle-brain connection for optimal movement efficiency)
Build strength, stability and the foundation to promote vibrant health.