The hamstrings have a long history of being the 'enemy' of good movement.
Tight, painful, cramping and all around bad guy, the poor old hammy cops a lot of negative press.
In this blog post, I wanted to share my thoughts with you about how to make friends with the hamstrings so you can all get on well together.
What are the hamstrings?
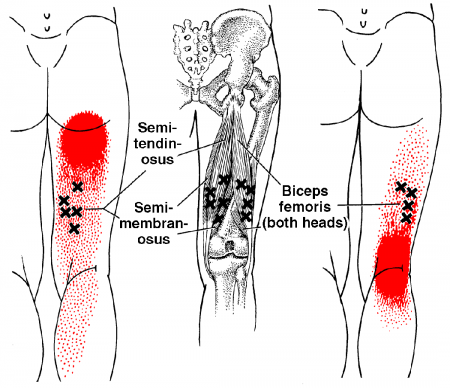
The hamstrings are made up of three muscles - the inside two are called the semimembranous and semitendinosus and the large outside hamstring is known as the biceps femoris.
The back of a right leg from hip to knee
In a bigger contex:
The Superficial Back Line, from Thomas Myers Anatomy Trains
The hamstrings are part of the Superficial Back Line - which is a myofascial line of tissue that incorporates the muscles and fascia from the bottom of the foot up to the back of the head.
When one area isn't functionally overly well, there will be compensations up or down the chain. Ever heard of hamstring issues affecting your lower back?
Tight hamstrings means that the instead of stretch and movement occurring through the back of the leg, the lower back gets compressed, especially when sitting or bending forwards.
That is one of the reasons we take a holistic view of your body and movement when you come in for an assessment. We leave no stone unturned in our quest to get to the source of your problem.
It doesn't matter where you feel your symptoms, we don't chase pain. We focus on finding the weak link/primary source and then allow your (powerful healing) body to do the rest.
"Where you think it is, it ain't" - Ida Rolf
What is the role of the hamstrings?
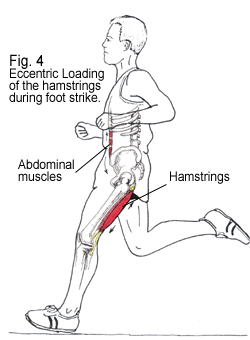
The primary role of the hamstrings in walking and running is to eccentrically control the landing of the foot. The hamstring complex undergoes a substantial eccentric contraction during the late swing phase (Yu et al, 2008) of gait.
Eccentric refers to a type of contraction where a muscle lengthens while contracting vs a concentric contraction where the muscle in contracting and shortening (e.g. doing a bicep curl).
As you can see, just before your foot lands, your knee is going from a bent position to an extended straight position and the hamstrings job is to allow for a controlled, smooth landing.
Whilst it is important to have adequate flexibility, the actual more important job of the hamstring to have enough strength and capacity to walk and run properly.
If a muscle doesn't have much capacity to contract when needed, it will most likely get overloaded. When it gets overloaded, it's muscle fibers contract and knot up, limiting flexibility.
For a runner, strength and stability trumps flexibility everyday of the week.
Trigger points in the hamstrings can refer pain to the upper thigh, buttock and around the knee
3 Steps To Making Friends With Your Hamstrings:
1. Stop stretching them.
Never again do a standing hamstring stretch. I don't mean avoid it for a few weeks or months.
I mean NEVER* do this stretch whilst you are alive on this planet!
Like an addict, you gotta give it up cold turkey.
Yes, you can still do yoga and downward dog and continue to move through functional range of movements but no mindless, static stretching.
Stretching in this position, you are actually making the hamstring weaker
Hang on a sec...I thought stretching was a good thing!?
Stretching the hamstring in this position, you are actually making the hamstring weaker and sending confusing mixed messages to the brain about what the function of the muscle is.
Anytime your brain is confused, it's going straight into fight-flight mode and will want to tighten everything up to protect it.
Intuitively stretching feels good and it often does give some short term relief.
But in the long run, with continued stretching, the hamstring becomes weaker and more likely to become overloaded and tight. Then you've got yourself into a real pickle.
The hamstring, once locked down, becomes an inefficient blob that hampers everything you try and do.
Our first step in making friends with the hamstring is to stop pissing it off, so no more stretching.
By the way, as an added bonus, your lower back pain and sciatica will thank you as the standing hamstring stretch has a good way of irritating it.
*If you desperately feel the need to stretch, then you can apply heat packs or use the foam roller/spiky ball directly on the muscle.
2. Reset.
To reset the hamstrings, I recommend first releasing the muscle with 3-4 sessions of deep tissue dry needling and myo-fascial release massage. This is like pushing re-set on your muscle tone and creating a fresh slate to work with. After a few sessions, the muscle will release and then we can move onto the final step.
It's important to get a twitch response that stimulates the blood flow and releases the chemicals in the muscle that have been holding it tight.
Be prepared for some significant post-treatment soreness for a 1-2 days. Months/years/decades of tightness ain't going down without a fight!
Check out more about dry needling here and see how it can get your healing on the fast track.
3. Build 'Em Back Up.
The biggest issue around the hamstring is it's near universal lack of strength.
When was the last time you did a specific hamstring strengthening exercise?
Most of us tend towards an excessive quads/hip flexors vs hamstrings ratio due to excess sitting, walking and running.
Quads are strong, hammies weak.
This imbalance is perceived by the hamstrings as threatening.
Powerfully contracting the quads during the running and kicking motion could potentially damage the hamstring.
How does the brain / muscle respond to threat?
You guessed - it tightens up.
Graduated Strengthening Program For Hamstrings:
The best long term strategy to make friends with your hamstrings is to build capacity so they can perform their job of eccentrically controlling the foot in landing.
If the hamstrings can happily do their job, they'll most likely start to feel safe, protected and will naturally start to release all on their very own.
Trust me, I'm a Physiotherapist!
It will take time (3-6 months) to build strength, so listen to your body and take it easy at the start. If you can only manage 2-3 reps in the beginning, that is fine. No rushing!
The goal is to push the hamstring to fatigue (feeling some hamstring soreness the following day is a good sign) and then allow it to adapt, recover and get stronger.
Make sure you create the right environment for healing via eating well (protein + vegies), drink plenty of water and get enough sleep.
Aim to do these strengthening exercises twice per week.
How many reps?
If you figure every 10k your run is approximately 5,000 steps on each side, then the hamstring needs a fair amount of endurance capacity. I would keep gradually increasing the reps until you are not feeling any pain on your walks and runs.
Quick note: avoid the hamstring curl machine at the gym. This exercise strengthens and shortens the hamstring, which is what you don't want.
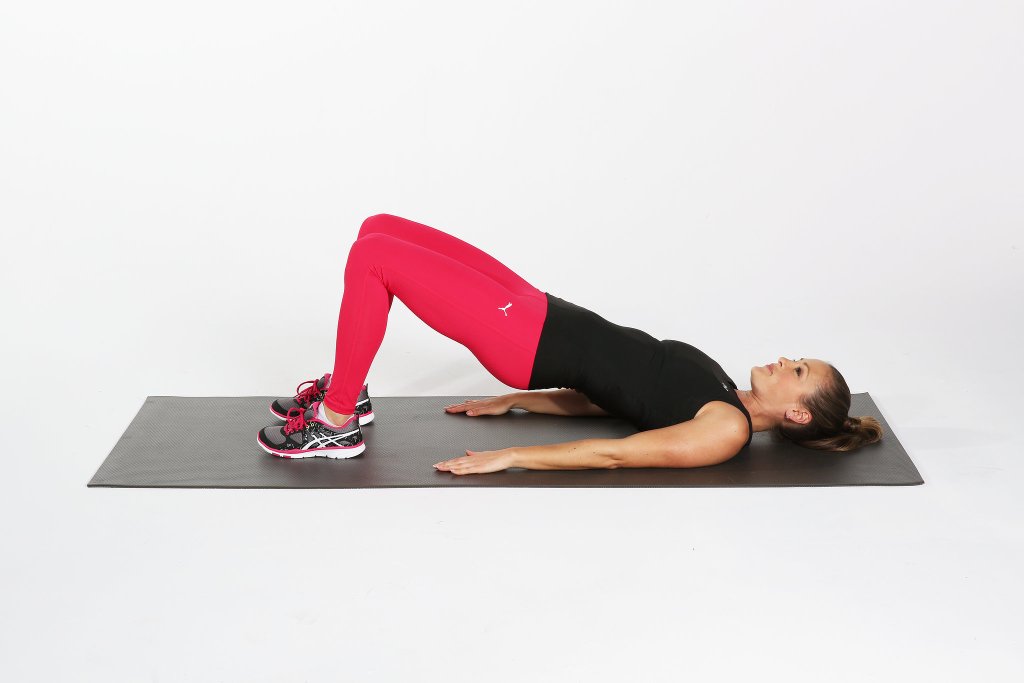
Step 1: Bridge
Try 3 x 30 sec holds. Relax your lower back and squeeze your glutes.
Tuck your pelvis so you feel the opening of the front of the hips.
Keep the bridge high as you extend one leg in front.
Hold for one breath and then switch sides. When you can repeat x 10 each side, move to step 2.
Step 2: Bridge on Foam Roller
Make sure the roller isn't too far away from you, otherwise the hamstrings will cramp.
The goal is to gradually build up the strength in the hamstrings. It may take 3-6 months so no rushing.
If you push too hard, then you most likely will lock the muscle down and you'll have to start over.
When you can complete 3 x 10 reps on each side, move onto step 3.
Step 3: Hamstring Curls on Swiss Ball
The perfect Eccentric Hamstring Exercise: Strengthening AND lengthening.
Quickly pull the ball in towards you and then SLOWLY (slow as you can) lower the ball away from you.
Count to as least 5 seconds as you do this.
Repeat until fatigue. and then do another x 2 rounds.
If you can do x 30 reps pretty easily, try one legged.
Practicing this movement will have a direct improvement on your hamstring problems, especially for runners.
Step Four: Single Leg Deadlift
Hold a dumbbell in each hand and stand on your right leg, lifting your left leg a few inches behind you (a). Keeping your back straight, lean forward from your hips until your body is almost parallel to the floor, the weights in line with your shoulders (b). Return to start. Do 12, then switch legs.
Bonus Tip:
Don't forget to strengthen the glutes, lower back and calf muscles above and below the hamstring. Often if these muscles have reduced capacity, the hamstring can become overloaded and then lock down.
So there you have it.
Have a go and please write in the comments how you get on.
I'd really appreciate your feedback :-)
References:
Hamstring muscle kinematics and activation during overground sprinting.
Yu B, Queen RM, Abbey AN, Liu Y, Moorman CT, Garrett WE. J Biomech. 2008 Nov 14;41(15):3121-6