If you walk into any gym, you may see someone sadistically foam rolling their ITB, making all sorts of interesting faces.
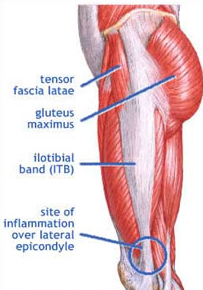
The ITB, if you are unsure, stands for Ilio-Tibial Band - that is the long fibrous tissue that runs from the hip down to the knee along the outside of your thigh (see pic below).
An irritated ITB can lead to pain and inflammation in the outside of the knee, especially in runners and cyclists. If not addressed early, this can lead to ongoing pain and can be tricky to manage.
To roll or not to roll?
Recently there has been a lot of noise being made about the fact that regular foam rolling and stretching doesn’t physically change the ITB at all.
Some researchers point out that it is impossible to ‘release’ your ITB with a foam roller because it takes thousands of kilograms of pressure to change it.
Proponents for the foam roller say that it helps keep the tightness under control and prevents runner’s knee.
Who is right?
Well yes the ITB is made from very tense connective tissue are it probably doesn’t change all that much. And I’d definitely agree you can easily stir things up if you are constantly and aggressively rolling.
And you don’t want to have super loose ITB’s either - having strong and resilient ITB’s are an important part strong and efficient running form.
Ideally, you want to have them ‘in-tune’ like a musical instrument - not too tight or too loose.
What is really happening when you roll?
While it is hard to say for sure, I suspect most of the benefits from foam rolling are coming from what lies directly under the ITB. Here you’ll find one of the quad muscles called the Vastus Lateralis (see diagram below).
When you look at the above picture, you could easily believe that the ITB is the main player on the outside of the thigh.
However, on closer inspection, the diagram below gives a much more accurate picture, showing the relative density of the ITB compared with the huge Vastus Lateralis (VL) on the left of the picture.
Cross section area: ITB vs VL (Vastus Lateralis)
As you can see, while the ITB gets all the attention, the vastus lateralis has a huge cross sectional area and is the real workhorse of the leg.
The vastus lateralis muscles tend to become overloaded with lots of downhill running, squats and lunges.
Some muscles in the body due to their anatomy and location, are impossible to stretch effectively. The vastus lateralis is one of them.
Over time, one of the most common causes of pain on the outer side of the knee is from a build-up of tightness in the vastus lateralis (see trigger point referral patterns below).
So learning how to maintain flexibility by foam rolling in this area is hugely important to keep your knee and hip joints moving well.
How to foam roll the Vastus Lateralis:
Benefits to foam rolling the ITB/vastus lateralis:
improved short term flexibility and blood flow
releasing the muscles under the ITB (Vastus lateralis)
stimulate the para-sympathetic system to activate the healing and recovery process
connecting with your body and bringing awareness to any overly sensitive or tight areas
Things to keep in mind:
avoid rolling directly over the outside of the knee and hip joints
should never feel more then 5/10 pain. Regulate the pressure by using your upper body and core if needed. In the words of John Rusin, “Stop mindlessly foam roll like a jackass.”
if you’re getting ongoing tightness, you need to get to the root cause! Consider contributing factors such as shoe wear (time for a new pair?), training habits, too many hills, inadequate glute strength and capacity, inadequate carbohydrates before and during your run, inadequate protein for recovery
don’t bother trying to actually stretch the ITB - it’s anatomy is too complex to get an effective stretch
When to roll:
if you have extremely tight leg muscles, you can roll gently before you exercise (30-60 secs max)
the best time to roll is after you have finished exercising, when the muscles are warmed up
Conclusion:
above all listen to your own body - if it feels good to you, then keep foam rolling your ITB and outer quads
don’t spend too long foam rolling (2-3 mins total time to roll the major muscle groups) after you exercise is enough, with perhaps one longer stretching session per week
an even more effective approach, target the vastus lateralis with the foam roller by rotating 45 degrees onto your front, and slowly bend and straighten your knee as you roll
if you’re getting ongoing tightness and pain in the ITB, seek professional help with a Physiotherapist to help identify contributing factors
Questions?
Please leave a comment below…
More from the blog: